What Is the Mental Healthcare Act 2017?
Are you aware of your rights concerning mental health and treatment in India? The Mental Healthcare Act, 2017 (MHCA) is a crucial law that regulates mental health care and treatment across the country. It adopts a significant rights-based approach, placing obligations on the government and professionals to protect the rights of individuals with mental illness.
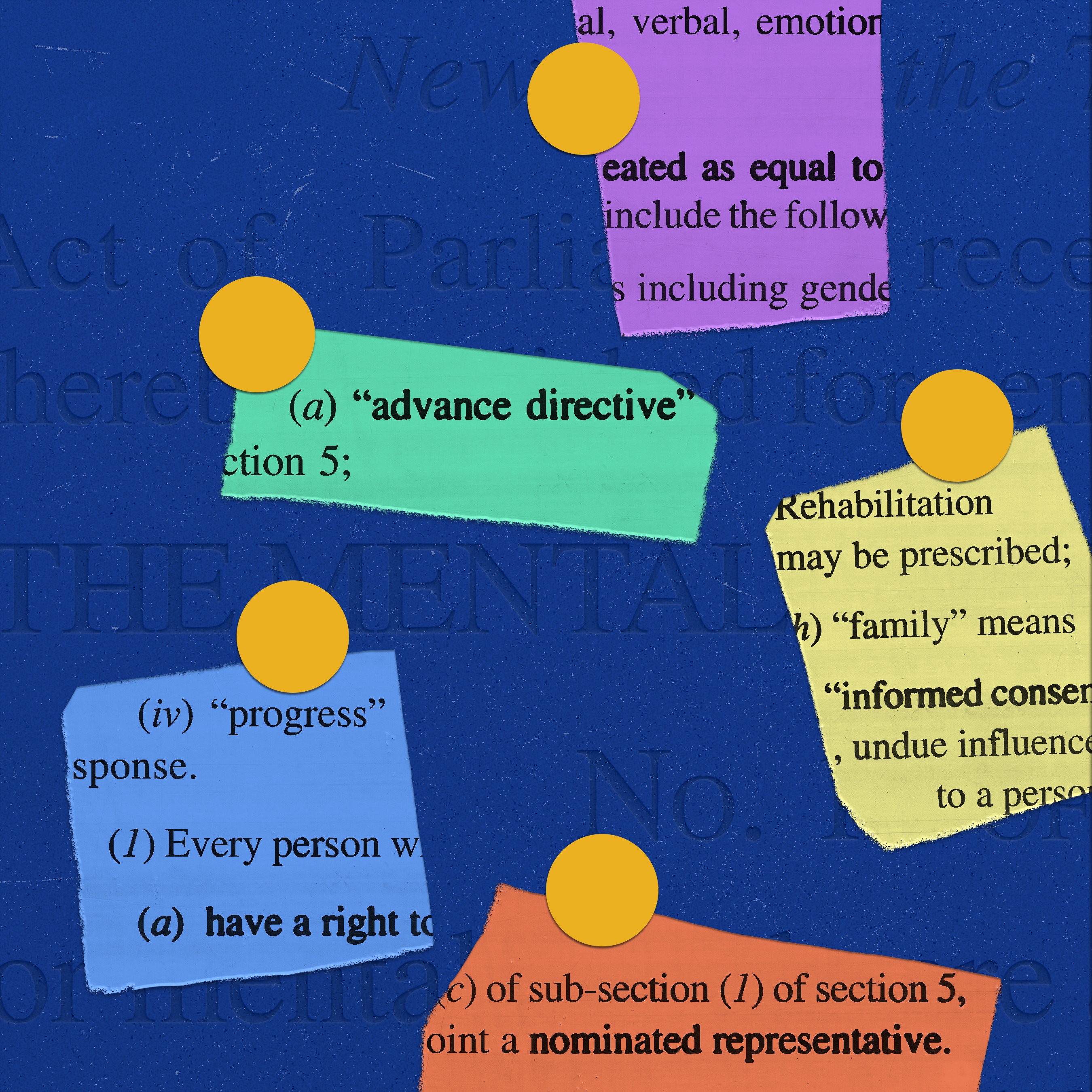
This Act outlines fundamental principles like equality, autonomy, dignity, full participation, and non-discrimination for all individuals, including decisions about their mental healthcare. It clarifies what constitutes a mental illness according to accepted medical standards and, most importantly, defines what is not considered a mental illness, such as a person's identity, beliefs, or past history of treatment.
The MHCA empowers individuals by emphasising concepts like ‘capacity’ and ‘informed consent’ for treatment. It also introduces important tools like ‘advance directives’, allowing individuals to state their future treatment preferences, and the role of a ‘nominated representative’ to support or make decisions when needed.
Furthermore, the Act details the essential rights of individuals with mental illness, encompassing everything from the right to equality and non-discrimination to the right to confidentiality, community living, access to information and medical records, legal aid, and protection from inhumane treatment. It requires medical insurers to provide coverage for mental illness treatment in the same manner as they do for physical illnesses and prohibits harmful practices such as solitary confinement or chaining.
The law also delineates the roles of key bodies such as the Mental Health Review Boards (MHRBs), which protect rights and address complaints, as well as the Central/State Mental Health Authorities (CMHA/SMHA), responsible for regulation and setting minimum standards for mental health establishments. It specifies the duties of police and magistrates in managing situations involving individuals with mental illness. Notably, it asserts that a person attempting suicide is presumed to be under severe stress and should not be punished.
Understanding the MHCA’s provisions is vital for ensuring respectful, rights-affirming mental healthcare. To gain a deeper understanding of these concepts, the types of admissions and treatment outlined by the Act, and the specific duties of the government and mental health professionals, we encourage you to explore two key resources:
- The comprehensive visual summary resource, a detailed guide for young people that unpacks India's Mental Healthcare Act, 2017.
- The Reference Manual for Mental Health Professionals, which offers practical guidance on the Act’s provisions and implementation.
Both documents provide essential insights into the law and how it protects rights of persons with mental illness.


